Digital speech signal processing
Brief description
The course introduces the basic techniques and theories of digital speech signal processing. The first part of the lecture focuses on the topic of "Hearing and Speech", which deals with the psychological effects of sound perception and speech generation. Discrete-time signals and systems and their computer-aided processing are then discussed. The non-parametric short-time analysis of speech signals, speech coding and IP telephony are further topics.
Lecture contents
- Speaking and listening
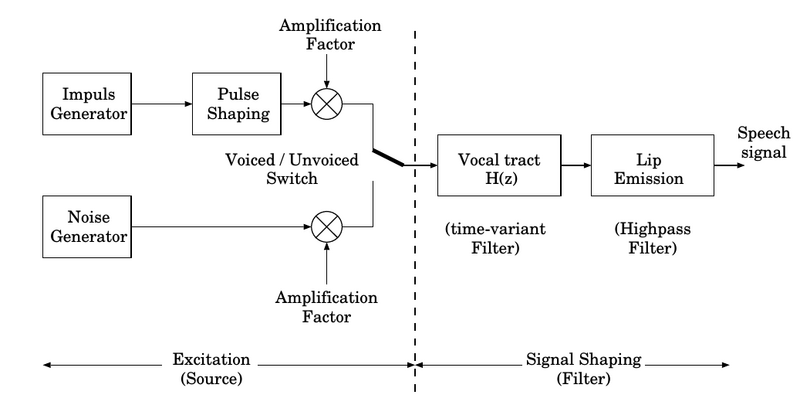
- Speech production: human speech organs, sound classes, source-filter model, vocoder
- Fundamentals of sound waves
- Hearing: human hearing organ, psychoacoustics and physiology of hearing, loudness, masking, frequency groups
- Discrete-time signals and systems
- Fundamentals: elementary signals, LTI systems
- Transformations: Fourier transform of discrete-time signals, discrete Fourier transform, FFT
- Realisation of discrete-time filtering in the frequency domain: overlap-add, overlap-save
- Statistical speech signal analysis
- Fundamentals of probability theory
- Short-term analysis of speech signals: spectrogram, cepstrum
- Estimation of speech signals
- Optimal filtering
- LPC analysis
- Spectral filtering for noise suppression: spectral subtraction, Wiener filtering
- Adaptive filtering: LMS adaptation algorithm, echo cancellation
- Speech coding
- Coding in the time domain: waveform coding, parametric coding, hybrid coding methods
- Coding in the frequency domain
- Amplitude quantisation: uniform quantisation, quantisation with companding (µlaw, alaw)
Specialist competences
After completing this course, students will be able to analyse digital signals, especially audio signals, in the time and frequency domain, efficiently represent speech signals and implement widely used algorithms for speech signal analysis and processing in the frequency or time domain.
Interdisciplinary competences & methodical implementation
Students are able to explain effects in real signals using theoretical knowledge, can analyse theoretical approaches through systematic consideration and are able to further their own education through the well-founded consideration of the content.
Teaching methods
- Lectures with blackboard and presentation
- Alternating theoretical and practical face-to-face exercises with exercise sheets and computers and
- Demonstrations of real systems in the lecture
Recommended reading
- P. Vary, U. Heute, W. Hess: Digitale Sprachsignalverarbeitung : Teubner Verlag 1998 : Good textbook
- J.R. Deller, J.G. Proakis, J.H.L. Hansen: Discrete-Time Processing of Speech Signals : IEEE Press, 2000 : General speech signal processing, also contains chapters on speech recognition
- Oppenheim, Schafer: Digital Signal Processing : Good book on digital signal processing
Classification
- Course for Master students
- ECTS: 6
- Language: German / English
- Semester: Summer term
Einordnung
- Veranstaltung für Master Studierende
- ECTS: 6
- Sprache: Deutsch oder Englisch
- Semester: Sommersemester
You are interested in: